Color mixing is one of the most fascinating aspects of art, design, and even science. Whether you are a painter, designer, or just curious about how colors work, knowing how to combine colors to get new colors can transform your creativity.
This guide explains the basics of color theory, primary colors, secondary colors, and advanced mixing techniques with practical tables and examples.
Table Of Contents
- Table Of Contents
- 1. What Is Color Mixing?
- 2. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Colors
- 3. How to Combine Colors: Color Mixing Chart
- 4. Additive vs Subtractive Color Mixing
- 5. How to Create New Colors with Paints
- 6. Digital Color Mixing (RGB vs CMYK)
- 7. Tips for Effective Color Combinations
- 8. FAQs on Color Mixing
- Final Thoughts
- Explore More on WHTYPE Blog :
1. What Is Color Mixing?
Color mixing means combining two or more colors to create new shades, tones, or tints. The process depends on the medium:
- Paint mixing (subtractive method) → Used in painting, printing, and dyes.
- Light mixing (additive method) → Used in digital screens, stage lighting, and photography.
2. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Colors
| Type of Color | Examples | How They Are Made |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Colors | Red, Blue, Yellow | Cannot be created by mixing other colors |
| Secondary Colors | Green, Orange, Purple | Made by mixing two primary colors |
| Tertiary Colors | Red-Orange, Yellow-Green, Blue-Purple, etc. | Made by mixing a primary and a secondary color |
These three groups are the foundation of the color wheel, which helps us understand how to combine colors.
3. How to Combine Colors: Color Mixing Chart
Here’s a simple color mixing chart for paints and pigments (subtractive color mixing):
| Color 1 | Color 2 | New Color Created |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Blue | Purple |
| Red | Yellow | Orange |
| Blue | Yellow | Green |
| Red | Green | Brown |
| Blue | Orange | Brown |
| Yellow | Purple | Brown |
| White | Any Color | Lighter Tint (e.g., Red + White = Pink) |
| Black | Any Color | Darker Shade |


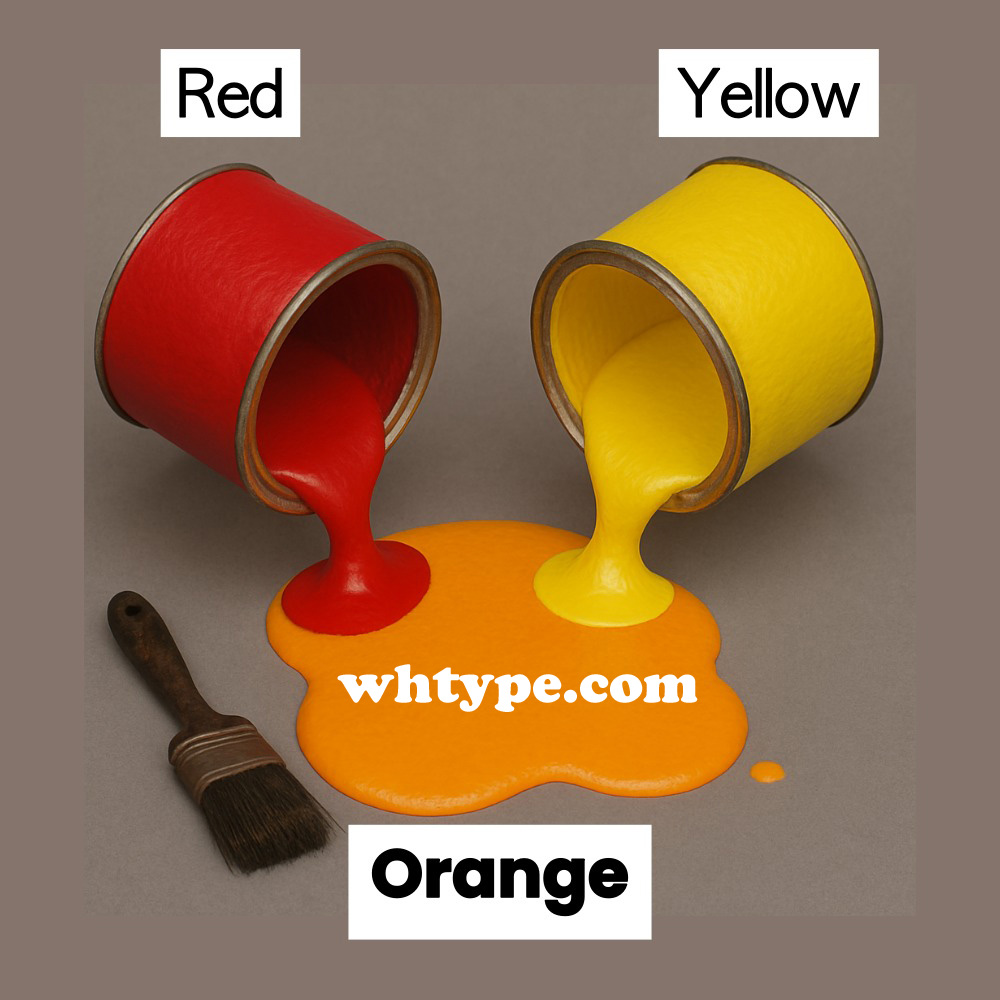





4. Additive vs Subtractive Color Mixing
| Feature | Additive (Light) | Subtractive (Paint/Pigment) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Colors | Red, Green, Blue (RGB) | Red, Yellow, Blue (RYB) / Cyan, Magenta, Yellow (CMY) |
| Result of All Colors | White light | Black/dark brown |
| Used In | Screens, LEDs, Photography | Paints, Printing, Dyes |
5. How to Create New Colors with Paints
When using paints:
- Mix complementary colors (colors opposite on the wheel) → neutral shades like brown or gray.
- Mix analogous colors (next to each other on the wheel) → harmonious blends.
- Use white and black to control brightness and depth.
6. Digital Color Mixing (RGB vs CMYK)
In digital design and printing, color models work differently:
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue) → Additive model used in screens.
- Red + Green = Yellow
- Green + Blue = Cyan
- Blue + Red = Magenta
- All combined = White
- CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black) → Subtractive model used in printing.
- Cyan + Magenta = Blue
- Magenta + Yellow = Red
- Yellow + Cyan = Green
- All combined = Black
7. Tips for Effective Color Combinations
- Use a color wheel to find complementary and harmonious shades.
- Test small amounts first before mixing large batches.
- Keep a record of your mixes (like recipes) for consistency.
- Balance warm and cool tones depending on the mood you want.
8. FAQs on Color Mixing
Q1: What two colors make purple?
Red + Blue = Purple.
Q2: How do you make pink?
Red + White = Pink.
Q3: Can you make primary colors by mixing?
No, primary colors (Red, Blue, Yellow in paints; RGB in light) cannot be created by mixing other colors.
Q4: How do designers mix colors digitally?
They use RGB values or Hex codes in software like Photoshop, Illustrator, or Canva.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how to combine colors to get new colors is the key to mastering painting, design, and digital creativity. Whether you use RYB, RGB, or CMYK models, the principles of color mixing remain universal. With practice, you can create endless shades and stunning combinations.










































































































Leave a comment